
Feed additives and growth promoters are attaining importance nowadays in the poultry industry because of their wide spectrum of beneficial impacts ranging from promoting growth and production to immune enhancement and health protection.Nutritionists are constantly working to provide feed that is better and more affordable. Good feed won't be enough to accomplish the task; it must also be used more effectively. Nutritionists and veterinary professionals have recently focused a lot of emphasis on poultry development promotion through correct nutrient utilisation and the use of probiotics.
The word “probiotic” means “for life”. According to the currently adopted definition by FAO/WHO, probiotics are: “live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host”. So, basically probiotic isa live microbial feed supplement which beneficially affects the host animal by improving its intestinal microbial balance. Probiotic species used in poultry nutrition mostly belongs to Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Bacillus, Bifidobacterium, Enterococcus, Aspergillus, Candida, and Saccharomyces.
Health benefits of probiotics and mechanisms of action
Over 2000 years ago, Hippocrates stated, “all diseases begin in the gut”. It is also said that afully fit digestive system is an amazing marvel of nature.
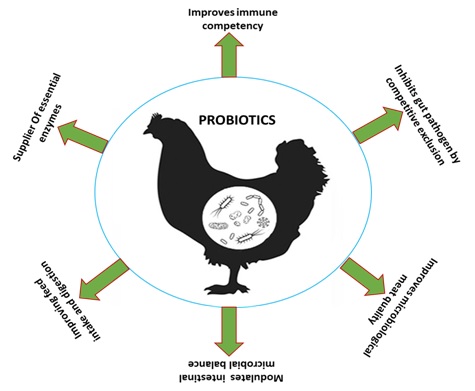
Probiotics have beneficial effect on broiler performance by modulation of intestinal microflora and pathogen inhibition. They are key players in supporting the entire digestion process.The mode of action of probiotics in poultry includes: (i) maintaining normal intestinal microflora by competitive exclusion and antagonism; (ii) improving feed intake and digestion (iii); altering metabolism by increasing digestive enzyme activity and decreasing bacterial enzyme activity and ammonia production; (iv) stimulating the immune system; (v) improving microbiological meat quality and (vi) modulating intestinal microbial balance.
The probiotics competes with other micro-organisms for nutrients, binding sites and receptors on intestinal mucosa and suppress the growth of pathogenic microbes by producing antimicrobial agents. The antagonistic activity of probiotics against pathogenic bacteria may also be mediated by modification of the immune system, formation of organic acids, lowering of gut pH, and stimulation of host defence mechanisms. Probiotics even produce their own enzymes, enabling birds to digest food more thoroughly.The enzymatic production by probiotic bacterial strains has caused rapid growth and advancement in the field of probiotics. Bacillus licheniformis strains have been heavily used in the industry because of its ability to produce amylase, protease, keratinase and B-mannase.
Probiotics are currently the main feed additives used in poultry industry because of their immense empirical benefits: improvement in the gut microbiological homeostasis, immune response, growth, and laying performances. In addition, the use of probiotics may address the public health concerns of antimicrobial resistance development to some extent, as this could replace the use of some subtherapeutic antibiotics used as growth promoters in poultry industry.